- Print
- DarkLight
- PDF
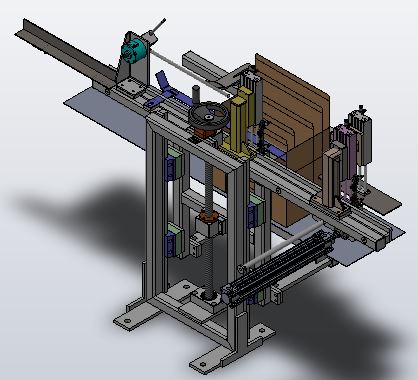
Introduction - Flap Folding Assembly
1. 3D Model
- Product Contact Parts - MS Powder Coated RAL 7045
- Product Non-Contact Parts - SS304
2.Flap Folding Operation
- Flap folding assembly folds & close the remaining flaps of the carton after MG insertion.
- This station also rejects carton (due to wrong sachet count or missing MG or carton improperly closed) off the main drive to a rejection conveyor by side shift
3. Maintenance
Important Precautions: -
READ this manual before operating or servicing this equipment.
- ALWAYS remove power and wait at least 30 seconds before connecting / disconnecting any internal harnesses. Failure to observe these precautions may result in damage to, or destruction of the equipment.
- ALWAYS take proper precautions when handling static sensitive devices.
- SAVE this manual for future reference.
- DO NOT allow untrained personnel to operate, clean, inspect, maintain, service or tamper with this equipment.
- DO NOT connect or disconnect any digital or analogue components to the equipment with power connected or damage may result.
Refer click the below Maintenance Schedule for Flap Folding
4. Spare Parts
Note: Click on the Description for the details about Spare Parts
ITEM | Description | Dwg No | Critical | Recommended |
11. | P205-1212 | X | ||
26. | P200-1010 |
| X | |
44. | I105-1002 |
| X | |
57. | ASV220F-M5-06 |
| X | |
| 58. | SMC Speed Controller AS2201F-01-06 | SMC.AS2201F-01-06 | X | |
63. | I117-9200 |
| X |
5.Risk Assessment
Risk Assessment or HAZOP, or a Hazard and Operability Study, is a systematic way to identify possible hazards in a work process. In this approach, the process is broken down into steps, and every variation in work parameters is considered for each step, to see what could go wrong.
Please refer the below attachment for HAZOP Document
6.Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting is the process of identifying, diagnosing, and resolving problems or issues that arise in various systems, equipment, or processes. it involves a systematic approach to problem-solving, using a combination of analytical, technical, and problem-solving skills.
The first step in troubleshooting is to identify the problem. This can involve gathering information about the issue, including when it started, what systems or equipment are affected, and any error messages or symptoms that are observed. Once the problem is identified, the next step is to diagnose the root cause. This involves analyzing the information collected and using technical knowledge to determine what is causing the issue. After the root cause is identified, the next step is to develop a plan for resolving the issue.
Refer the below about the Troubleshooting.
.jpg)